What is a HEPA Air Purifier Filter?
HEPA (High-Efficiency Particulate Air) filters are mechanical air filters that meet rigorous standards of efficiency set by international organizations. To qualify as true HEPA, filters must capture at least 99.97% of particles that are 0.3 microns in diameter (the most penetrating particle size, or MPPS). This performance standard was originally developed by the U.S. Atomic Energy Commission during World War II to protect researchers from radioactive particles.
Modern HEPA Filters consist of a mat of randomly arranged fibers, typically made from fiberglass with diameters between 0.5 to 2.0 microns. The filter media is pleated to increase surface area, with typical pleat depths ranging from 5mm to 300mm. The air space between fibers is much larger than the particles they capture, relying on three mechanisms: interception, impaction, and diffusion.
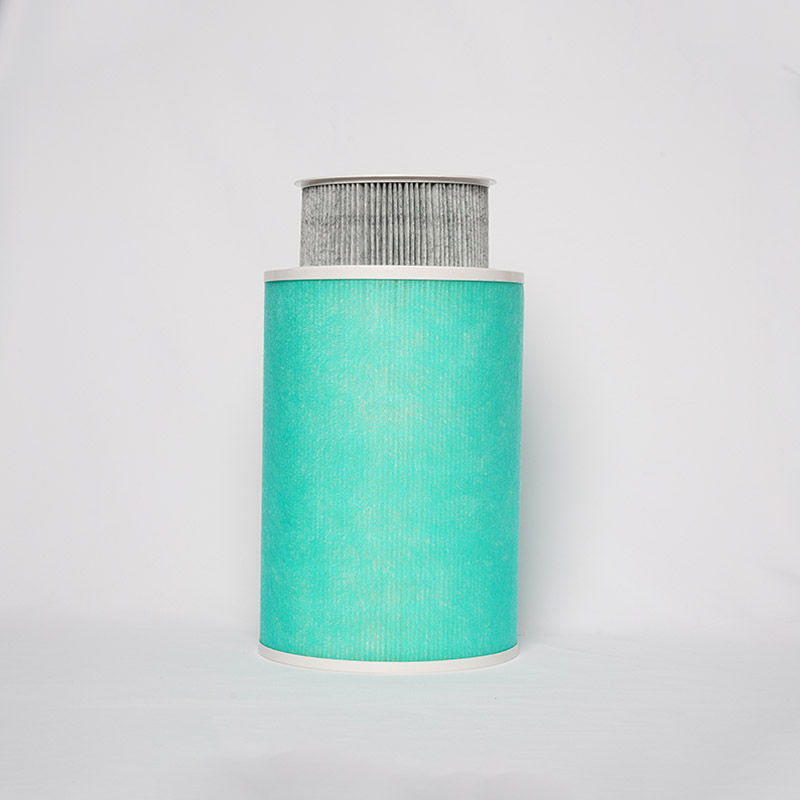

Key Technical Characteristics of HEPA Filters
1. Filtration Efficiency
True HEPA Filters demonstrate ≥99.97% efficiency at 0.3 microns. Some advanced variants achieve even higher performance:
HEPA H13 (EN1822 standard): 99.95% efficiency
HEPA H14: 99.995% efficiency
ULPA (Ultra Low Penetration Air) filters: 99.999% at 0.12 microns
2. Pressure Drop and Airflow
The pressure drop across a clean HEPA filter typically ranges from 100 to 300 Pascals at rated airflow. This increases as the filter loads with particles, with most systems designed to operate effectively up to 600-800 Pa before requiring replacement.
3. Dust Holding Capacity
High-quality HEPA filters can hold between 100 to 300 grams of particulate matter before reaching terminal pressure drop, with industrial-grade filters capable of holding up to 1 kilogram.
4. Microbial Filtration Efficiency
HEPA filters demonstrate exceptional performance against biological contaminants:
Bacteria (0.3-10 microns): >99.99% capture
Viruses (0.005-0.3 microns): 95-99.9% capture (many attach to larger particles)
Mold spores (1-30 microns): >99.97% capture
Primary Applications of HEPA Air Purifiers
1. Healthcare Facilities
Hospitals use HEPA filtration in:
Operating rooms (minimum 20 air changes per hour)
Isolation rooms for immunocompromised patients
Pharmaceutical compounding areas (ISO Class 5 environments)
2. Residential Use
Home applications focus on:
Allergy relief (removing pollen at 10-100 microns)
Asthma management (capturing 0.5-5 micron particulates)
Pet dander reduction (2.5-10 micron particles)
3. Industrial Applications
Critical manufacturing environments require HEPA filtration:
Semiconductor cleanrooms (Class 1 to Class 1000)
Aerospace component manufacturing
Pharmaceutical production (GMP compliance)
4. Commercial Buildings
Modern HVAC systems incorporate HEPA in:
Airport terminals (processing 50,000+ CFM)
Museums and archives (protecting artifacts)
Data centers (preventing equipment contamination)
Maintenance and Care for HEPA Filters
1. Replacement Schedule
Follow manufacturer guidelines, typically:
Residential: 6-12 months
Commercial: 3-6 months
Healthcare: 1-3 months
Use particle counters or pressure drop measurements for precise determination.
2. Cleaning Procedures
Most HEPA filters are not washable, but some models allow surface vacuuming:
Use a HEPA-rated vacuum with soft brush attachment
Limit cleaning to once between replacements
Never use water or cleaning solutions on standard HEPA media
3. Handling Precautions
Proper handling maintains filter integrity:
Wear gloves to prevent oil transfer from skin
Inspect for damage before installation
Seal used filters in plastic bags for disposal
4. System Maintenance
Complementary maintenance tasks:
Clean pre-filters monthly
Check fan motors and bearings annually
Monitor system airflow rates quarterly
Note: Some newer "washable HEPA" filters use alternative materials like thermobonded polypropylene, which can withstand gentle washing (typically ≤40°C water with mild detergent). However, these generally have slightly lower initial efficiency (95-99% at 0.3 microns) and degrade with each cleaning cycle.